To receive these weekly articles, subscribe here.
This article is from the new book Innovative Leadership for Health Care. The book was written by Maureen Metcalf of Innovative Leadership Institute and several other co-authors, to provide health care workers with frameworks and tools based on the most current research in leadership, psychology, neuroscience, and physiology to help them update or innovate how they lead and build the practices necessary to continue to update their leadership skills. It is a companion to the interview on Innovating Leadership, Co-creating Our Future between Dr. Neil Grunberg, one of the co-authors, and Maureen titled Innovative Leadership for the Health Care Industry that aired on Tuesday, March 23rd, 2021.
The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation’s Urban Institute reports that on an average night in the United States, around 465,000 people will go to sleep in our hospital beds. They will wear our gowns, eat food prepared in our kitchens, have their faces washed with water from our sinks. Some will undergo lifesaving procedures; some will undergo preventative observation, all will be in a state of vulnerability, unlike almost any other experience. Many will receive the care they would term as “miraculous.” Whether it is inside one of our 6,100 hospitals or in a rural office 100 miles from the nearest metro emergency room, health care is a big responsibility. It is always intimate. It is always humbling. It is often urgent.
Advances in training, education, information, public policy, and technology account for many of these daily miracles. We assert these miracles are also the result of extraordinary leadership. Leadership leveraging the strength of the team to go beyond the limitations of the individual. Leadership creating resources when and where they are needed. Leadership reaching beyond what can be touched and extending to the health care delivery system.
Just as receiving health care is intimate, humbling, and often urgent, so is leadership development. This book provides the education and tools to help you grow personally and increase your knowledge and skills. If you are not touched as well as challenged, lost as well as enlightened, and reflective as well as affirmed, then we have failed you. Leadership growth is a contact sport. Changing who you are is the real leadership growth that you seek. Creating miracles for your patients, staff, and community is your reward for risking this personal leadership journey.
Health care professionals are highly respected and valued in society. They have essential, existential roles as healers of the sick and injured and promoters of physical and mental health. Effective health care professionals apply their knowledge and skills appropriately and ethically. They respect colleagues, patients, patients’ significant others, and the limits of their knowledge and skills. They are leaders in that they are aspirational and inspirational. They influence these stakeholders and the organization’s cultures and systems in which they have a formal leadership role. They lead themselves, their people, their teams, and their organizations.
Becoming a better health care leader and optimizing innovation hinge on your ability to authentically examine your inner makeup and diligently address some challenging limitations. Leadership innovation or elevating your leadership quality can be accelerated by a structured process involving self-exploration, allowing you to enhance your leadership beyond tactical execution. While we provide a process, we want to be clear that readers should use this process to be effective for them. We each face different challenges and relate to leadership development in different ways. Each of us will use this book slightly differently. With that in mind, we tried to create a framework that is actionable and easy to follow. The process of leadership growth can be challenging, especially when it requires exploration of implicit beliefs and assumptions and potential changes to your overall worldview. Combining health care leadership with innovation requires you to transform the way you perceive yourself, others, and your role as a health care leader.
Wiley W. Souba noted, “Unless one knows how to lead one’s self, it would be presumptuous for anyone to be able to lead others effectively… Leading one’s self implies cultivating the skills and processes to experience a higher level of self-identity beyond one’s ordinary, reactive ego level… To get beyond their ‘ordinary, reactive ego,’ effective leaders relentlessly work on ‘unconcealing‘ the prevailing mental maps that they carry around in their heads. This unveiling is critical because leaders are more effective when they are not limited by their hidden frames of reference and taken-for-granted worldviews. This new way of understanding leadership requires that leaders spend more time learning about and leading themselves.”
By earnestly looking at your own experience—including motivations, inclinations, interpersonal skills, proficiencies, and worldview, and aligning them with the context in which you operate—you can optimize your effectiveness in the current dynamic environment. Through reflection, you learn to balance the hard skills you have acquired through experience with the introspection attained through in-depth examination—all the while setting the stage for further growth. In essence, you discover how to strategically and tactically innovate and elevate leadership the same way you innovate in other aspects of your profession.
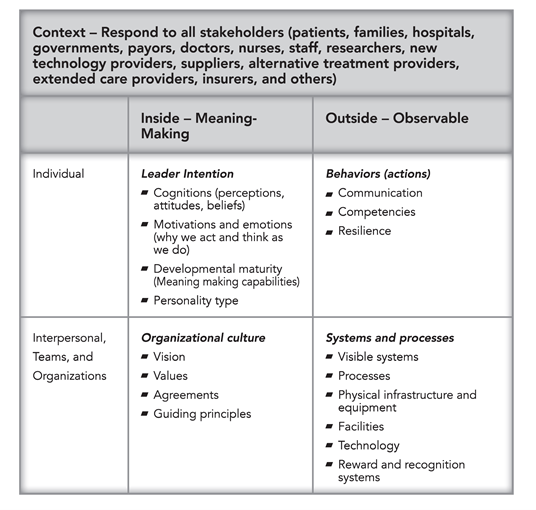
We define leadership using the following chart. Leaders must attend to and align all elements of the overall system continually to respond to changes within the system and external factors within your context, such as insurers and government regulations.
This table is foundational to depict how we talk about the facets of the leader’s self and organization. When one facet changes, the leader must realign other aspects to ensure efficient and effective operation. Many leadership programs focus on leadership behaviors; this book is different in that it addresses where the leader fits within the overall system and how they are responsible for leading.
- The upper left quadrant reflects the inner meaning-making of each leader (the personal). It contains both innate and developed capacities. This quadrant provides the foundation of self-awareness and individual development. It serves as the basis for behavior, competence, and resilience. Leaders must be aware of their inner landscape to be truly effective.
- The upper right quadrant reflects observable behaviors, actions, competencies, and communication. This quadrant is what we see in leaders. Leadership training often focuses on checklists of behaviors because they are easier to assess and discuss. This book is different; it suggests actions, but it is not prescriptive. We acknowledge that behaviors tie to your meaning-making, culture, systems, and processes.
- The lower left quadrant is inside the groups (interpersonal/dyads, teams, and organizations). It includes the vision, values, agreements, guiding principles, and other factors that create health care cultures.
- The lower right quadrant reflects the visible systems, processes, physical infrastructure and equipment, facilities, technology, and reward and recognition systems
Part of what is innovative about this approach is that it requires leaders to focus on all four areas concurrently. When one area changes, others are impacted. When leaders’ beliefs change, their behaviors often change. Behavior changes impact culture and systems. The same is true when the organization changes, such as shelter in place during a pandemic. Health care leaders need to change their behaviors and face new challenges, such as telemedicine’s increasing use. One essential leadership skill is to quickly realign across all four quadrants in response to changes in any single quadrant.
Innovative health care leaders influence by equally engaging their personal intention and action with the organization’s culture and systems to move the health care organization forward to improve the lives of the people it serves. These leaders also take into consideration the rightful interests of the organizational members. Depending on the role of leaders and sphere of influence, they impact individuals, teams, and the entire organization. Health care professionals who are innovative leaders adapt and develop themselves and their organizations to optimize effectiveness with changing environments or contexts (psychological, social, physical). This book guides health care professionals in becoming Innovative Health Care Leaders.
To find out more about this new book, Innovative Leadership for Health Care, click here. To find out how to implement this innovative book into your health system, contact Innovative Leadership Institute here
Check out the companion interview and past episodes of Innovating Leadership, Co-creating Our Future, via iTunes, TuneIn, Stitcher, Spotify, Amazon Music, and iHeartRADIO. Stay up-to-date on new shows airing by following the Innovative Leadership Institute LinkedIn.
About the Authors
Maureen Metcalf, M.B.A., founder and CEO of the Innovative Leadership Institute, is a highly sought-after expert in anticipating and leveraging future business trends.
Erin S. Barry, M.S. is a Research Assistant Professor in the Department of Military and Emergency Medicine at the Uniformed Services University.
Dukagjin M. Blajak M.D., Ph. D. is an Associate Professor and H&N Division Director in the Radiation Oncology department at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute.
Suzanna Fitzpatrick, D.N.P., ACNP-BC, FNP-BC, is a senior nurse practitioner at the University of Maryland Medical Center in Baltimore, Maryland.
Michael Morrow-Fox, M.B.A., ED.S., is a consultant with the Innovative Leadership Institute experienced in health care, education, banking, government, and non-profit management.
Neil Grunberg, Ph.D., is Professor of Military & Emergency Medicine, Medical & Clinical Psychology, and Neuroscience in the Uniformed Services University (USU) of the Health Sciences School of Medicine; Professor in the USU Graduate School of Nursing; and Director of Research and Development in the USU Leader and Leadership Education and Development (LEAD) program, Bethesda, Maryland.